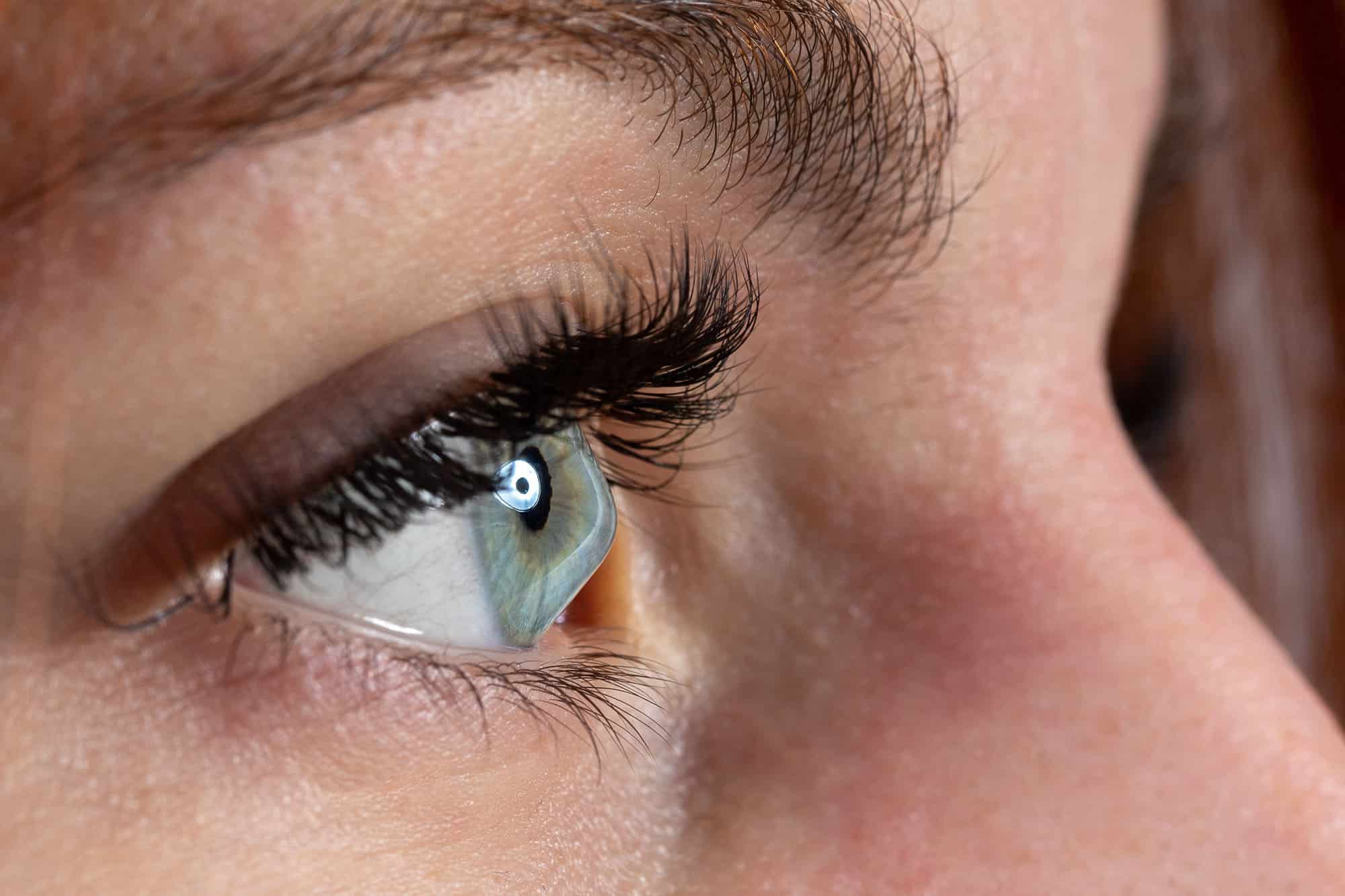
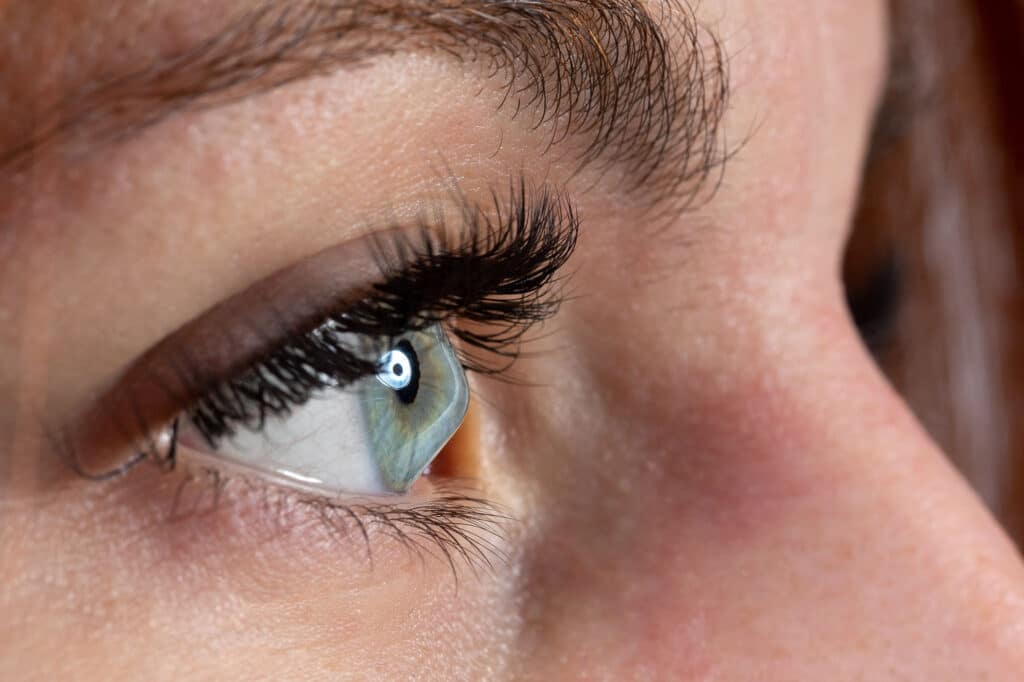
Keratoconus is a progressive eye condition that causes the cornea, the clear front part of the eye, to thin and bulge into a cone-like shape. This irregular shape can significantly impair your vision, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks such as reading, driving, or even recognizing faces. Left untreated, keratoconus can continue to worsen, leading to further vision problems and even the need for a corneal transplant.
Fortunately, there are several treatment options available for keratoconus, and one effective procedure is called corneal cross-linking (CXL). This treatment aims to strengthen and stabilize the cornea, preventing it from further thinning and bulging, and in some cases, even reversing the effects of keratoconus.
What is Corneal Cross-Linking (CXL) Surgery?
Corneal cross-linking is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a combination of ultraviolet (UV) light and a photosensitizing eye drop called riboflavin (vitamin B2) to create new chemical bonds, or “cross-links,” within the cornea. This process helps to strengthen and stabilize the cornea, effectively halting the progression of keratoconus..
Understanding the Science Behind Corneal Cross-Linking
The cornea is composed of collagen fibers, which are responsible for maintaining the cornea’s shape and structural integrity. In individuals with keratoconus, these collagen fibers become weakened and less organized, leading to the characteristic thinning and bulging of the cornea.
Corneal cross-linking works by using UV light and riboflavin to create new chemical bonds between the collagen fibers, effectively strengthening and stabilizing the cornea. This process can increase the cornea’s resistance to further deformation and progression of keratoconus.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Traditional Cross-Linking Procedure
Here’s what you can expect when you are scheduled to undergo corneal cross-linking:
- Numbing the Eye: The procedure begins with the administration of numbing eye drops to ensure your comfort throughout the procedure.
- Removing the Corneal Epithelium: The outermost layer of the cornea, known as the epithelium, is gently removed using a specialized instrument.
- Applying Riboflavin Eye Drops: Once the epithelium has been removed, a series of riboflavin eye drops are applied to the cornea. The riboflavin acts as a photosensitizer, allowing the UV light to create the necessary cross-links within the cornea.
- Exposing the Cornea to UV Light: After the riboflavin has been absorbed into the cornea, the eye is exposed to a controlled amount of UV light for a specific duration, typically around 30 minutes. This UV light activation triggers the cross-linking process, strengthening the cornea.
- Applying Protective Contact Lens: At the end of the procedure, a protective contact lens is placed on the eye to aid in the healing process and provide comfort during the initial recovery period. Eventually the epithelium will grow back.
Recovery and Aftercare Following Corneal Cross-Linking
After the corneal cross-linking procedure, you can expect some discomfort and sensitivity to light, which is normal and to be expected. Your eye doctor will provide you with specific instructions for your post-operative care, which may include the use of antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops, as well as the wearing of the protective contact lens.
It’s important to follow your eye doctor’s instructions carefully during the recovery period, as this will help ensure the best possible outcome and minimize the risk of any complications. The full recovery process can take several weeks, and you may experience some temporary vision changes during this time.
Success Rates and Effectiveness of Corneal Cross-Linking for Keratoconus
Studies like this one have demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of corneal cross-linking in halting the progression of keratoconus. While the primary goal of the procedure is to halt the progression of keratoconus and prevent further vision loss, in some cases, it has been shown to not only stabilize the cornea but also improve visual acuity and reduce the need for other interventions.
The Future of Corneal Cross-Linking and Advancements in Treatment
As research and technology continue to advance, the field of corneal cross-linking is expected to see further improvements and refinements. At the CLEI Center for Keratoconus, we currently offer both standard and specialty cross-linking, and we are dedicated to leading the way in CXL treatment. Our involvement in clinical trials is ongoing, and our range of trials continues to grow. To discover the best cross-linking option for your needs, book an appointment with one of our keratoconus specialists today.
Conclusion: The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment for Keratoconus
Early diagnosis and treatment of keratoconus are crucial for preserving your vision and preventing the condition from progressing to more advanced stages. Corneal cross-linking has emerged as a highly effective and safe treatment option, offering the potential to halt the progression of keratoconus and, in some cases, even improve the shape and function of the cornea.
If you or a loved one have been diagnosed with keratoconus, it’s important to consult with an experienced eye care professional to discuss the available treatment options and determine the best course of action for your individual needs. With the right care and treatment, you can take an active role in managing your keratoconus and maintaining your vision for years to come.Take the first step towards preserving your vision and improving your quality of life – contact us today to schedule your appointment.